IPSec
Release time:Dec 20, 2017
1.Basic Introduction
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) protocol is a common security protocol on the Internet. It is the most widely used security protocol standard in the development of VPN technologies in various network security solutions. It has a wide range of Mechanism and strong security.
2.Application
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) protocol is a common security protocol on the Internet. It is the most widely used security protocol standard in the development of VPN technologies in various network security solutions. It has a wide range of Mechanism and strong security.
2.Application
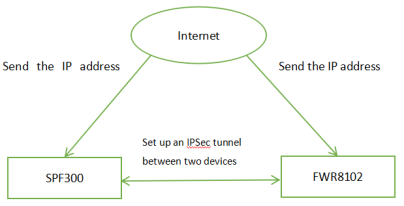
An underlying issue between IPSec tunnels and dynamic routing protocols is that dynamic routing relies on multicast or broadcast packets for routing reachability notification, whereas IPSec tunnels do not support multicast or broadcast packet encryption. Our company put forward the solution to this problem by adopting the combination of GRE and IPSec to make the configuration easier.
GRE configuration of the device:
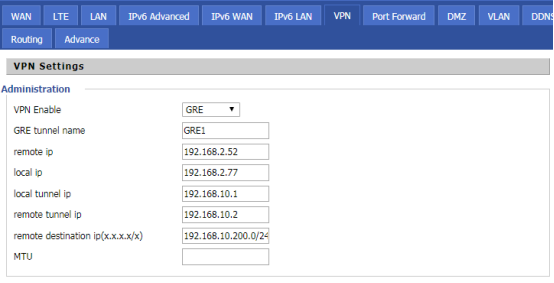
Device 1

Device 2
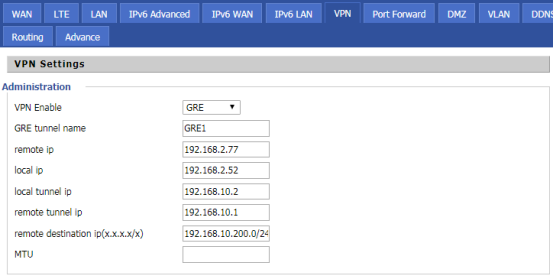
| Parameter | Description |
| VPN Enable | Enable VPN Enable, select GRE |
| GRE tunnel name | Fill in the tunnel name |
| Remote IP | Fill in Remote IP |
| Local IP | Fill in Local IP |
| Local tunnel IP | Fill in the IP of the local tunnel |
| Remote tunnel IP | Fill in the IP of the opposite tunnel |
| Remote destination | Fill in the destination segment |
IPSec configuration
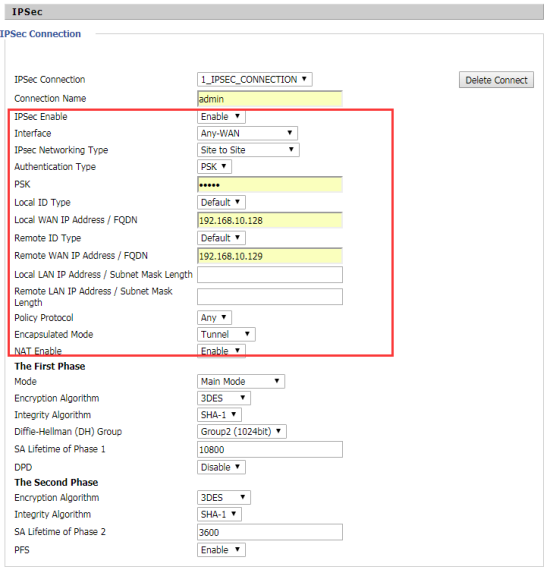
| Parameter | Description |
| IPSec Connection | Select the IPSec connection name or create a new IPSec |
| Connection name | Fill in the IPSec connection name |
| IPSec enable | Enable IPSec |
| Interface |
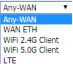 Select the type of connection for IPSec Select the type of connection for IPSec
|
| IPSec Networking Type | Choose IPSec networking mode, there are two options, one is the way to the site, the other is from the remote access |
| Authentication Type | The type of authentication here can only be pre-shared key option |
| PSK | Fill in a password, the remote password and the local password must be the same |
| Local ID Type | Choose one of the three types Default / FQDN / ID as the local ID |
| Local WAN IP Address/FQDN | Fill in the address of the local device WAN |
| Remote ID Type | Choose one of the three types Default / FQDN / ID as the remote ID |
| Remote WAN IP Address/FQDN | Enter the IP address of the remote device that establishes the tunnel with the local device |
| Local LAN IP Address/Subnet Mask Length | Enter the length of the subnet mask of the local area network |
| Remote LAN IP Address/Subnet Mask Length | Fill in the length of the subnet mask of the peer LAN |
| Policy Protocol | Choose a policy agreement, any or L2TP |
| Encapsulated Mode | IPSec has two encapsulation modes, one is tunnel mode and the other is transmission mode. The purpose of transmission mode is to protect end-to-end secure communication. The purpose of tunnel mode is to protect certain or all data between stations. Users can According to their actual needs of choice model. |
| NAT Enable | Select to enable or disable NAT disability |
| The First Phase | |
| Mode | The first phase of the model there are two, one is the main mode, one is the savage mode (also known as the positive mode) |
| Encryption Algorithm |
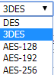 Choose the encryption algorithm you need Choose the encryption algorithm you need
|
| Integrity Algorithm | There are two authentication algorithms, one is SHA-1 and the other is MD5 |
| Diffie-Hellman (DH) Group |
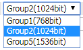 Choose one of three key patterns from the algorithm Choose one of three key patterns from the algorithm
|
| SA Lifetime of Phase 1 | The life cycle of SA is 10800 by default, you can set it yourself |
| DPD | Select to enable or disable DPD, the default DPD is disabled |
| The Second Phase | |
| Encryption Algorithm |
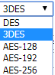 Choose the encryption algorithm you need Choose the encryption algorithm you need
|
| Integrity Algorithm | There are two authentication algorithms and the first phase, one is SHA-1, the other is MD5 |
| SA Lifetime of Phase 2 | The life cycle of SA is 10800 by default, you can set it yourself |
| PFS | Select to enable or disable PFS, the default DPD is Enabled. |










 Back to list
Back to list